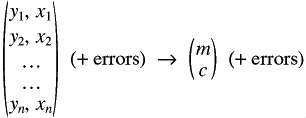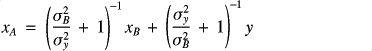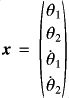Some Fundamentals of
INVERSE MODELLING
Ross Bannister
Room 2L49, Dept. of Meteorology
D.A.R.C.
University of Reading
'Sky and Water I', M.C. Escher, 1938
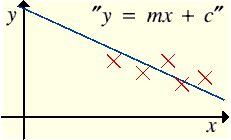
What does an inverse model do?'Forward' model
'Inverse' model
Examples of inverse modelling ...
... and any situation in where:
|
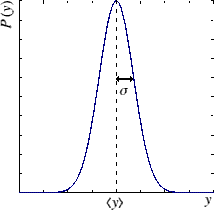
Parameter Estimation by Maximum Likelihood (Method of Least Squares)Gaussian error characteristics (one variable)
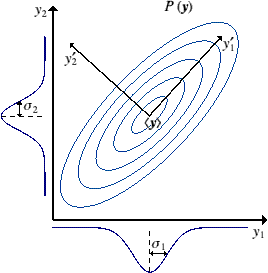
(two or more variables)
|
Ingredients (for an inversion)
The forward model (strong constraint) How will 1,2,3 combine to give the most likely set of parameters?Bayes' Theorem:
Maximum likelihood = minimum penalty
|
Notes on the cost function
For
Why "least squares"?
Eg. if
|
Methods of Inverting
|
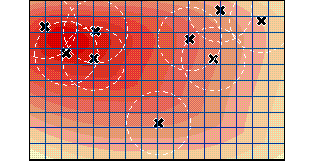
|
|
2. Best Linear Unbiased Estimator (BLUE)
|
|
|
3. Variational Analysis (4d-Var)
![]()
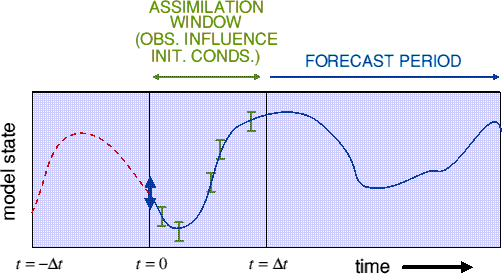
- Account taken of errors.
- Can use indirect obs. and non-linear operators.
- Suitable for large Nos. of degrees of freedom.
- 4d-Var is dynamically consistent.
- A-priori in data poor regions.
- Difficult to know
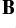 .
.
- Expensive.
- Difficult to implement and use.
- Needs preconditioning.
4. Kalman filter
- Account taken of errors.
- Can use indirect obs.
- A-priori in data poor regions.
- Evolves
 in time.
in time.
- Difficult to use with non-linear operators.
- Very expensive.
- Difficult to use practically.
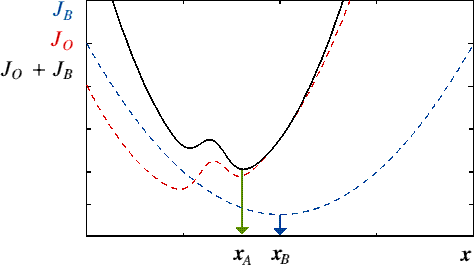
Example with BLUE
1 unknown parameter, 1 observation, 1 initial estimate
BLUE formulae:
|
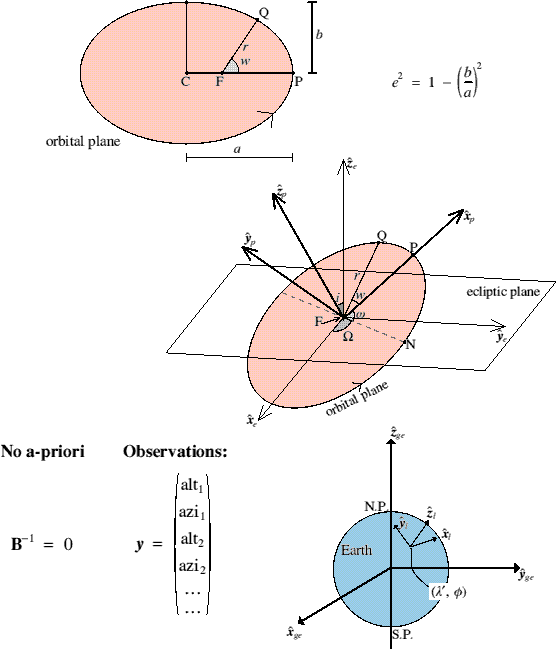
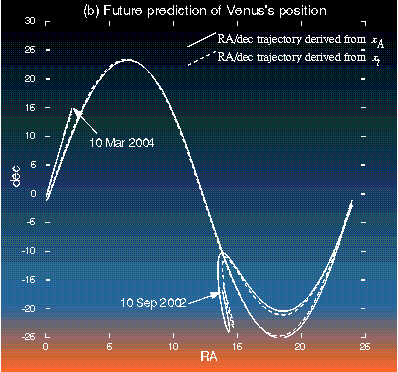
Example with BLUE(Astronomy - Inverting Kepler's Equation) Want to determine orbital parameters:
Physics of the forward model:
|
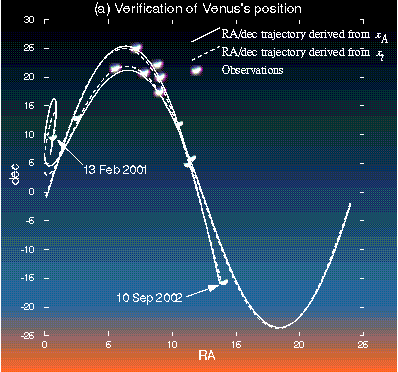
Inversion results
|
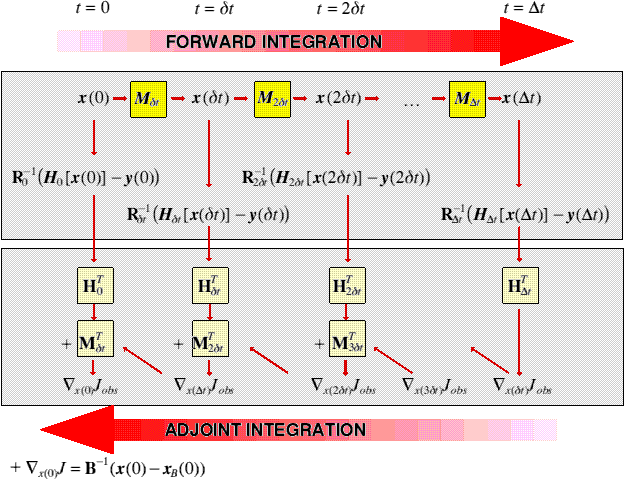
4-Dimensional Variational Data AssimilationLeith, 1993:... the atmosphere "is a chaotic system in which errors introduced into the system can grow with time ... As a consequence, data assimilation is a struggle between chaotic destruction of knowledge and its restoration by new observations."
|
Schematic limb radiance operator
|
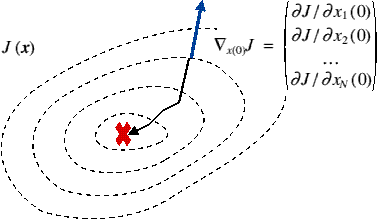
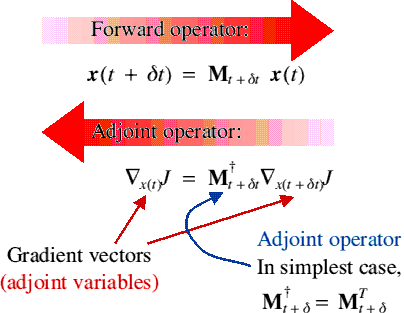
Adjoint Variables and Adjoint Operators
The adjoint of an operator propagates the adjoint variables in the reverse sense (this is just the chain rule generalised to many variables)
|
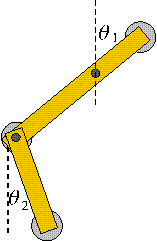
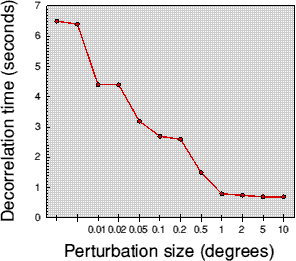
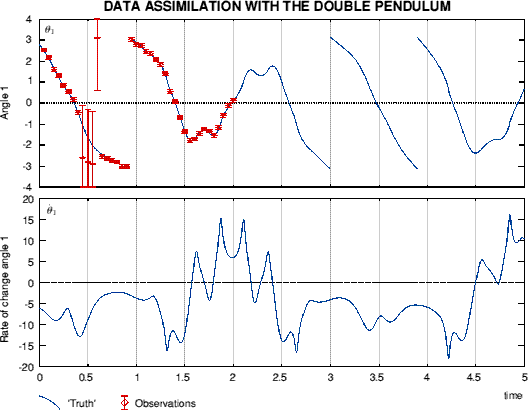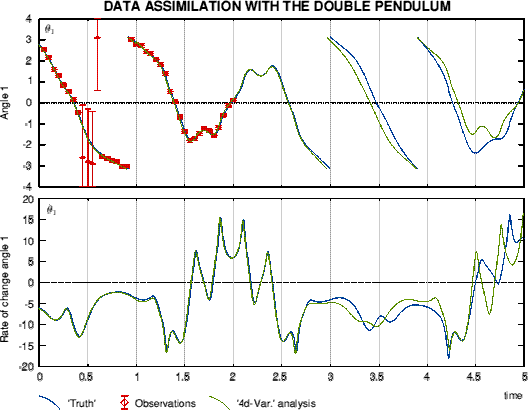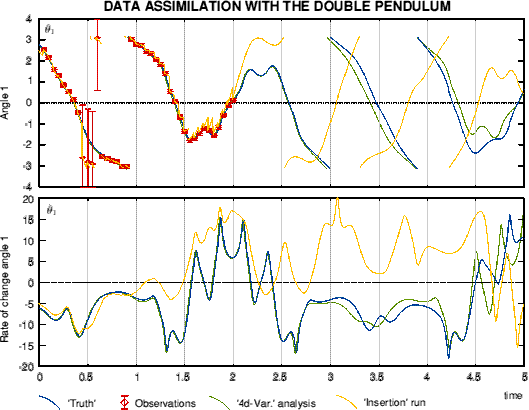
Example of '4d'-Var. with a simple chaotic systemThe double pendulum
|
Other GFD applicationsSources/sinks determinationForward model (tracer transport Eq.):
What are the sources/sinks,
Cost function:
Gradient w.r.t.
|
Other bonuses of doing inverse modelling / DA
Some difficulties with inverse modelling / DA
|
SummaryInverse methods:
|